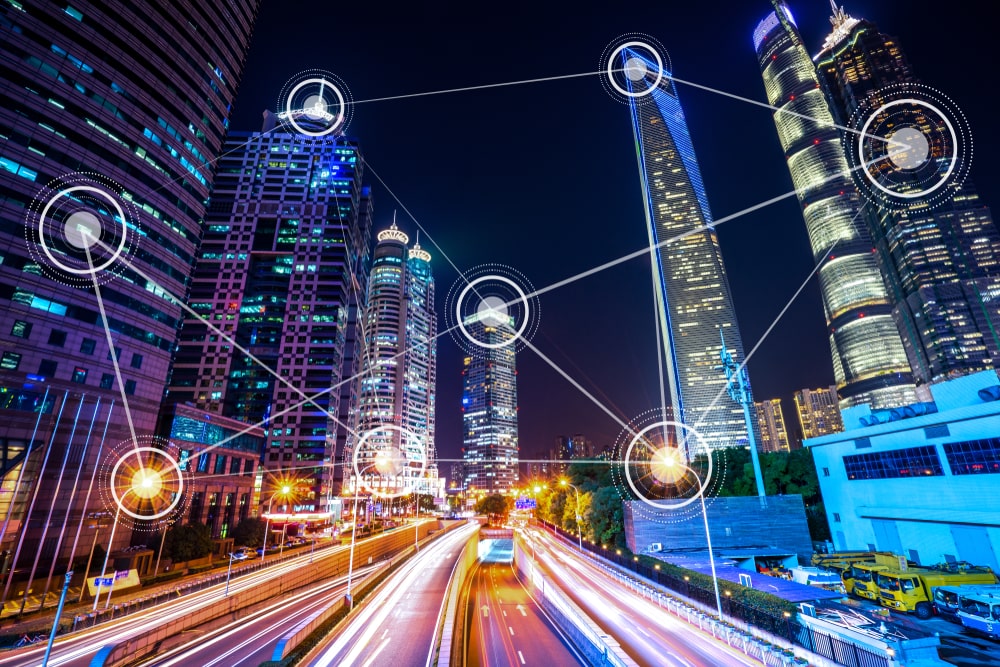
New technologies have not only changed the way industry professionals operate, but have additionally enhanced their ability to determine needs accurately and efficiently. The result is the development of a new generation of construction, which works more efficiently and sustainably.
Sensors
The widespread use of low-cost sensors and Internet of Things (IoT) devices has contributed to the development of smart manufacturing. These devices collect real-time data on various parameters such as structural conditions, temperature, humidity, air quality and occupant movement. The availability of these sensors allowed an unprecedented production capability during both the construction and operational phases of buildings.
Download images
Affordable high-quality cameras, combined with drones, airplanes and satellites, have revolutionized smart infrastructure. These cameras play a key role in monitoring the safety of workers during construction and help detect accidents and improve safety in smart construction sites, smart buildings and smart cities. Images, combined with sensors and models, provide a comprehensive understanding of the environment, leading to better decision making and problem solving.
Wireless communication
The always-on wireless Internet infrastructure, driven by 4G and 5G technology, facilitates the transmission of real-time data from sensors, IoT devices, and cameras to centralized GIS-based control systems. This constant connectivity enabled decision-making and automation, informed by the data collected from the entire infrastructure.
Advanced 2D and 3D visualizations
The development of advanced 2D and 3D parametric functions in design and modeling tools has accelerated the progress of smart infrastructure. These tools effectively create detailed infrastructure representations, allowing stakeholders to assess project viability and identify potential issues prior to construction. Integrating IoT and sensor data into these models enables real-time monitoring, maintenance prediction, and infrastructure optimization simulations.
BIM - models, modeling and management
Building information modeling (BIM) combines geometric data and design properties to create 3D models of buildings, roads, utilities and other infrastructure projects. It provides stakeholders with a geometrically accurate framework for collaboration and integration of IoT devices and sensors. The rich data provided by BIM models enables detailed monitoring, predictive maintenance and the creation of safer, more sustainable and resilient infrastructure. When combined with GIS, they can create an environment-sensitive, real-time dashboard.BIM - models, modeling and management: Building information modeling (BIM) combines geometric data and design properties to create 3D models of buildings , roads, utilities and other infrastructure projects. It provides stakeholders with a geometrically accurate framework for collaboration and integration of IoT devices and sensors. The rich data provided by BIM models enables detailed monitoring, predictive maintenance and the creation of safer, more sustainable and resilient infrastructure. When combined with GIS, they can create an environment-sensitive, real-time dashboard.
Capture and map reality
Reality capture technologies such as laser scanning and photogrammetry have transformed infrastructure data collection, ensuring unparalleled accuracy. When these technologies are combined with GIS systems, they provide accurate data for construction, remodeling and facility management workflows. A close match between the right representations and the real environment improves decision-making throughout the life cycle of the facility.
GIS and Location Intelligence
A particularly important tool is GIS, which acts as an aggregator of systems, data and processing in smart infrastructure projects. It helps project teams select and evaluate sites based on geography, resources, and environmental factors. By integrating all of the aforementioned technologies, real-time geographic analysis can be performed on construction sites, optimizing operations for efficiency, safety, and resource management. GIS technology plays a key role in real-time construction monitoring, allowing managers to project managers to identify and correct design deviations, streamline decision making and save time and resources. In addition, it helps create digital twins to effectively manage facilities, reducing operating costs, improving sustainability and demonstrating the importance of technology for smart infrastructure.
Those technologies have enabled professionals to make informed decisions, optimize manufacturing processes, improve safety and create a more efficient manufactured industry. If we also consider the cost reduction, environmental benefits and improvement they can bring to the quality of life of users of the built environment, the use of technology goes beyond facilitating the construction process and evolves into a meaningful, rational choice.